
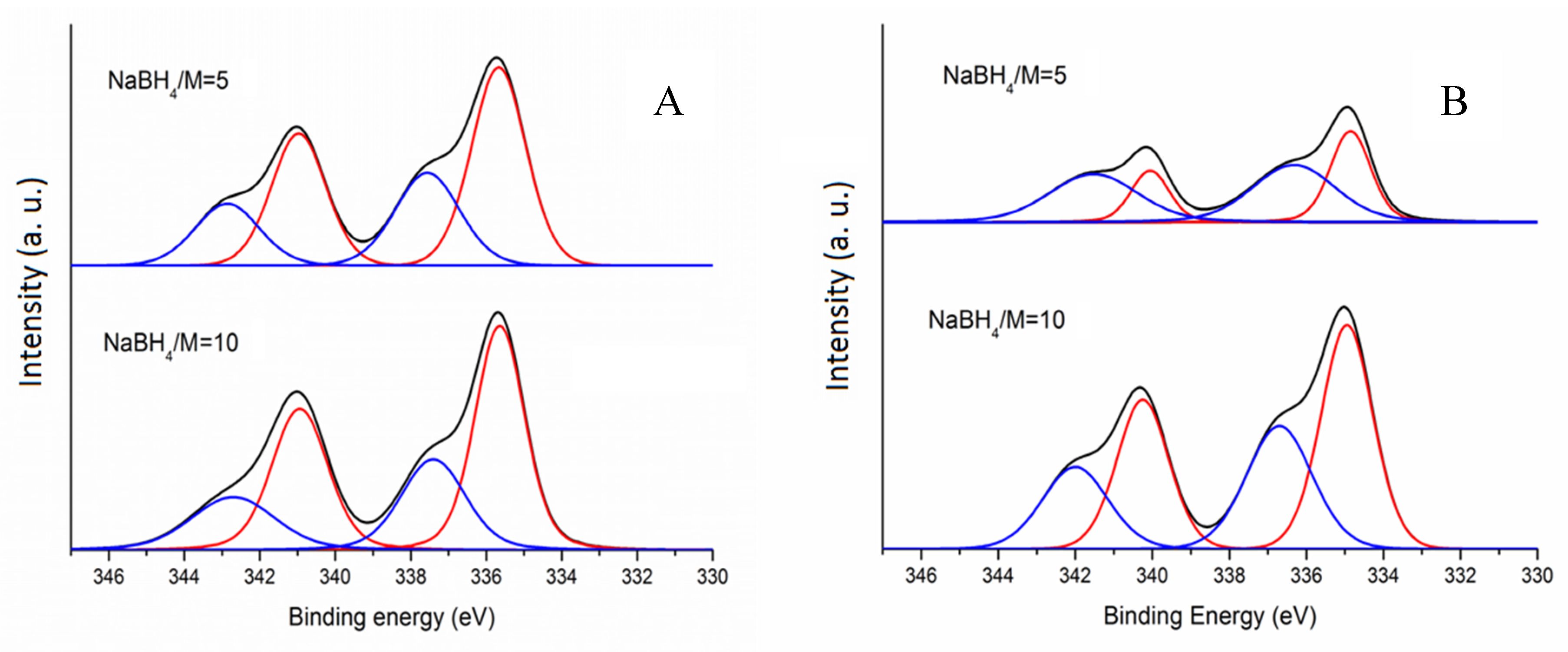
This work opens a rational approach to achieve the selective adsorption and expediting of polysulfide transition for the performance enhancement of Li-S batteries.
The constructed cathode delivers an areal capacity of 9.43 mAh cm -2 at 0.1 C at S loading of 6.8 mg cm -2, and it exhibits a gravimetric capacity of 1104 mAh g -1 with a capacity fading rate of 0.045% per cycle over 50 cycles at 0.2 C at S loading of 2.0 mg cm -2. The synthetic electrocatalyst deployed in the sulfur cathode plays a multifunctional role: (i) selectively adsorbing the polysulfides dissolved in the electrolyte, (ii) expediting the sluggish liquid-solid phase transformations at the active sites as electrocatalysts, and (iii) accelerating the kinetics of the electrochemical reaction of multielectron sulfur, thereby inhibiting the dissolution of LiPSs. Here, we report that Ni hexatomic clusters embedded in a nitrogen-doped three-dimensional (3D) graphene framework (Ni-N/G) possess stronger interaction with soluble polysulfides than that with insoluble polysulfides. The shuttle effect hinders the practical application of lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries due to the poor affinity between a substrate and Li polysulfides (LiPSs) and the sluggish transition of soluble LiPSs to insoluble Li 2S or elemental S.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
